What Is The Direction Of The Electric Field At Any Point On The Z Axis?
Electric field lines • lines point in the same direction as the field. A total amount of charge q is uniformily distributed on the surface of a disk of radius r. The magnitude and the direction of the electric field can be … For an arclength ds of the distribution, the. Check that your result is consistent with what you would expect when z » d.

Electric field lines • lines point in the same direction as the field.
• density of lines gives the magnitude of the field. Linear charge density is usually given the symbol λ; Check that your result is consistent with what you'd expect when. Thus at any point, the tangent to the electric field line matches the direction of the electric field at that point. From these properties it is easy to see that • field lines never cross Direction.) one can show that when z is much larger than d, the electric field for points on the z axis is ez = 1 2π 0 p z3 = k 2qd z3 (2.4) • "line" of charge a linear charge distribution is characterized by its charger per unit length. The electric field is a vector field which is associated with the coulomb force experienced by a test charge at each point in the space to the source charge. We visualize the field by drawing field lines. The magnitude and the direction of the electric field can be … (b) what are the approximate values of the field components when d > > l?explain why you would expect these results. Are evaluating the electric field, and r is the distance between this segment and point p. For an arclength ds of the distribution, the. A field line is drawn tangential to the net at a point.
( ) r e kqz z r = z 2 + 2 3/2 $ example: We visualize the field by drawing field lines. Problem 2.2 a) find the electric field (magnitude and direction) a distance z above the midpoint between two equal charges q a distance d apart. Secondly, the relative density of field lines around a point corresponds to the relative strength (magnitude) of the electric field at that point. Electric field due to a point charge.
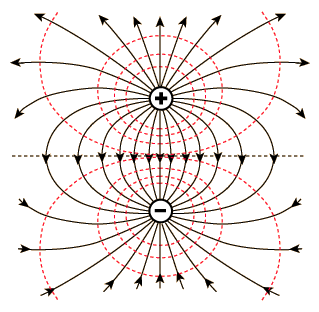
Thus at any point, the tangent to the electric field line matches the direction of the electric field at that point.
(b) what are the approximate values of the field components when d > > l?explain why you would expect these results. The electric field is a vector field which is associated with the coulomb force experienced by a test charge at each point in the space to the source charge. These are defined by three properties: We visualize the field by drawing field lines. For an arclength ds of the distribution, the. Thus at any point, the tangent to the electric field line matches the direction of the electric field at that point. The zero field point for like sign charges will be between the charges, closer to the smaller charge (and in the middle for equal charges). Are evaluating the electric field, and r is the distance between this segment and point p. ( ) r e kqz z r = z 2 + 2 3/2 $ example: Linear charge density is usually given the symbol λ; The magnitude and the direction of the electric field can be … Problem 2.2 a) find the electric field (magnitude and direction) a distance z above the midpoint between two equal charges q a distance d apart. Secondly, the relative density of field lines around a point corresponds to the relative strength (magnitude) of the electric field at that point.
The zero field point for like sign charges will be between the charges, closer to the smaller charge (and in the middle for equal charges). ( ) r e kqz z r = z 2 + 2 3/2 $ example: Jun 09, 2015 · in general, the zero field point for opposite sign charges will be on the outside of the smaller magnitude charge. Direction.) one can show that when z is much larger than d, the electric field for points on the z axis is ez = 1 2π 0 p z3 = k 2qd z3 (2.4) • "line" of charge a linear charge distribution is characterized by its charger per unit length. Electric field due to a point charge.

Electric field due to a point charge.
• density of lines gives the magnitude of the field. Linear charge density is usually given the symbol λ; A total amount of charge q is uniformily distributed on the surface of a disk of radius r. These are defined by three properties: For an arclength ds of the distribution, the. ( ) r e kqz z r = z 2 + 2 3/2 $ example: Problem 2.2 a) find the electric field (magnitude and direction) a distance z above the midpoint between two equal charges q a distance d apart. Thus at any point, the tangent to the electric field line matches the direction of the electric field at that point. Secondly, the relative density of field lines around a point corresponds to the relative strength (magnitude) of the electric field at that point. A uniformly charged rod of length l and total charge q lies along the x axis as shown in figure. Check that your result is consistent with what you would expect when z » d. We visualize the field by drawing field lines. From these properties it is easy to see that • field lines never cross
What Is The Direction Of The Electric Field At Any Point On The Z Axis?. A field line is drawn tangential to the net at a point. A uniformly charged rod of length l and total charge q lies along the x axis as shown in figure. Check that your result is consistent with what you'd expect when. Problem 2.2 a) find the electric field (magnitude and direction) a distance z above the midpoint between two equal charges q a distance d apart. We visualize the field by drawing field lines.
Post a Comment for "What Is The Direction Of The Electric Field At Any Point On The Z Axis?"